Diabetes : Types and Managing Strategies
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high levels of glucose in the blood. It affects millions of people worldwide and can lead to serious complications if not managed properly. Understanding the different types of diabetes and adopting appropriate management strategies is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. In this article, we’ll explore the various types of diabetes and effective ways to manage this condition.

Types of Diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
- Individuals with type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy to manage their blood sugar levels.
- This type of diabetes typically develops during childhood or adolescence, although it can occur at any age.
- Type 2 Diabetes:
- Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for the majority of cases.
- It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
- Risk factors for type 2 diabetes include obesity, sedentary lifestyle, family history, and age.
- Management of type 2 diabetes often involves lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes, regular exercise, weight management, and medication if necessary.
- Gestational Diabetes:
- Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth.
- It occurs when the body is unable to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands of pregnancy.
- Gestational diabetes can increase the risk of complications for both the mother and baby if not properly managed.
- Treatment may involve dietary adjustments, monitoring blood sugar levels, and, in some cases, insulin therapy.
Management Strategies for Diabetes:
- Healthy Eating:
- Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Avoiding sugary and processed foods can prevent spikes in blood sugar and promote overall health.
- Regular Exercise:
- Engaging in regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity and can lower blood sugar levels.
- Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling.
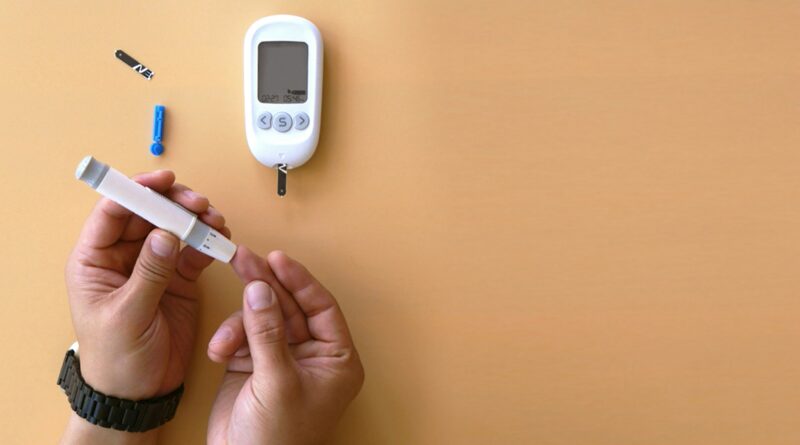
- Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels:
- Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for managing diabetes effectively.
- Use a glucose meter to track blood sugar levels and make adjustments to medication, diet, and activity levels as needed.
- Medication:
- Some individuals with diabetes may require medication to help control their blood sugar levels.
- Medications may include oral glucose-lowering drugs, insulin injections, or other injectable medications that stimulate insulin production or improve insulin sensitivity.
- Stress Management:
- Chronic stress can contribute to elevated blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes.
- Practice stress-reducing techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies to promote relaxation and overall well-being.
- Regular Medical Check-ups:
- Regular visits to healthcare professionals are important for monitoring diabetes-related complications and adjusting treatment plans as needed.
- Screenings for conditions such as eye disease, kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease are essential for early detection and management.
Conclusion:
Diabetes is a complex condition that requires lifelong management to prevent complications and maintain quality of life. By understanding the different types of diabetes and adopting effective management strategies such as healthy eating, regular exercise, medication, and stress management, individuals with diabetes can lead fulfilling lives and reduce their risk of complications. Working closely with healthcare professionals and staying informed about the latest advancements in diabetes management is key to successfully managing this condition